C Libraries¶
Not all of the libC is supported. The library is under development, and the intention is to make the library as complete as possible. There will be occasions, where the libc functions can’t be implemented, or have to differ from the standard.
stdio.h¶
In contrast to the C standard, fputc and fgetc are built-in functions, you do not need to include stdio.h to use them.
The globals stdin and stdout should be set to an input or output by the user.
The fputs function prints string to the output handle.
void fputs(unsigned string[], unsigned handle);
The fgets function reads a line, up to maxlength characters, or a line end from the input handle. The string will be null terminated. maxlength includes the null character.
void fgets(unsigned string[], unsigned maxlength, unsigned handle);
The puts function prints string to stdout.
void puts(unsigned string[]);
The gets function reads a line, up to maxlength characters, or a line end from stdin. The string will be null terminated. maxlength includes the null character.
void gets(unsigned string[], unsigned maxlength);
The getc returns a single character from stdin.
unsigned long getc();
The putc writes a single character to stdout.
void putc(unsigned c);
print.h¶
The fprint_decimal function prints a number in decimal to the output handle.
void fprint_decimal(int value, unsigned handle);
The fprint_hex function prints a number in hexadecimal format to the output handle.
void fprint_hex(int value, unsigned handle);
The fprint_float function prints a floatin point number to the output handle.
void fprint_float(float value, unsigned handle);
The print_decimal function prints a number in decimal to standard output.
void print_decimal(int value);
The print_hex function prints a number in hexadecimal format to standard output.
void print_hex(int value);
The print_float function prints a floatin point number to standard output.
void print_float(float value);
To provide flexibility, the definition of standard output is left to the user, it could be a serial port, an LCD display, or perhaps a telnet session. To define standard output assign it to an output.
#include <print.h>
stdout = output("uart_tx");
print_string("Hello World!\n"); //Hello World!
print_decimal(12345); //12345
print_hex(127); //7f
print_float(1.0); //1.0
scan.h¶
The fscan_hex function reads a hex value from the input handle.
int fscan_hex(unsigned stdin);
The fscan_decimal function reads an integer from the input handle.
int fscan_decimal(unsigned stdin);
The fscan_decimal function reads an float from the input handle.
float fscan_float(unsigned stdin);
The scan_hex function reads a hex value from standard input.
int scan_hex();
The scan_decimal function reads an integer from standard input.
int scan_decimal();
The scan_decimal function reads an float from standard input.
float scan_float();
To provide flexibility, the definition of standard input is left to the user. To define standard input, assign an input to the global stdin.
ctypes.h¶
The isalnum function returns 1 if c is an aphanumeric character otherwise 0.
unsigned isalnum(char c);
The isalpha function returns 1 if c is a letter otherwise 0.
unsigned isalpha(char c);
The islower function returns 1 if c is a lower case letter otherwise 0.
unsigned islower(char c);
The isupper function returns 1 if c is an upper case letter otherwise 0.
unsigned isupper(char c);
The isdigit function returns 1 if c is a digit otherwise 0.
unsigned isdigit(char c);
The isxdigit function returns 1 if c is a hexadecimal digit otherwise 0.
unsigned isxdigit(char c);
The isgraph function returns 1 if c is a printing character not including space otherwise 0.
unsigned isgraph(char c);
The isspace function returns 1 if c is white space character otherwise 0.
unsigned isspace(char c);
The isprint function returns 1 if c is a printing character otherwise 0.
unsigned isprint(char c);
The ispunct function returns 1 if c is punctuation otherwise 0.
unsigned ispunct(char c);
The toupper function returns the upper case equivilent of c if any otherwise c.
unsigned toupper(char c);
The tolower function returns the lower case equivilent of c if any otherwise c.
unsigned tolower(char c);
math.h¶
All angles are expressed in radians.
The M_LOG2E constant respresents an approximation of log_{2} e.
const float M_LOG2E
The M_LOG10E constant respresents an approximation of log_{10} e.
const float M_LOG10E
The M_LN2 constant respresents an approximation of log_{e} 2.
const float M_LN2
The M_LN10 constant respresents an approximation of log_{e} 10.
const float M_LN10
The M_PI constant respresents an approximation of 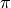 .
.
const float M_PI
The M_PI_2 constant respresents an approximation of \pi/2.
const float M_PI_2
The M_PI_4 constant respresents an approximation of \pi/4.
const float M_PI_4
The M_1_PI constant respresents an approximation of 1/\pi.
const float M_1_PI
The M_2_PI constant respresents an approximation of 2/\pi.
const float M_2_PI
The M_2_SQRTPI constant respresents an approximation of 2/\sqrt{\pi}.
const float M_2_SQRTPI
The M_SQRT2 constant respresents an approximation of \sqrt{2}.
const float M_SQRT2
Return the cos x.
float cos(float x);
Return the sin x.
float sin(float x);
Return the tan x.
float tan(float x);
Return the sinh x.
float sinh(float x);
Return the cosh x.
float cosh(float x);
Return the tanh x.
float tanh(float x);
Return the asinh x.
float asinh(float x);
Return the acosh x.
float acosh(float x);
Return the atanh x.
float atanh(float x);
Return the absolute value of float n.
float fabs(float n);
Return the absolute value of int n.
int abs(int n);
Return the e^x.
float exp(float x);
Return the log_{e} n.
float log(float n);
Return the log_{10} n.
float log10(float n);
Return the log_{2} n.
float log2(float n);
stdlib.h¶
Return the maximum value returned by the rand function.
const unsigned long RAND_MAX
Set the random seed to s.
void srand(unsigned long int s);
Return a random integer in the range 0 \le x \le RAND\_MAX.
unsigned long rand();
